Quick Enquiry
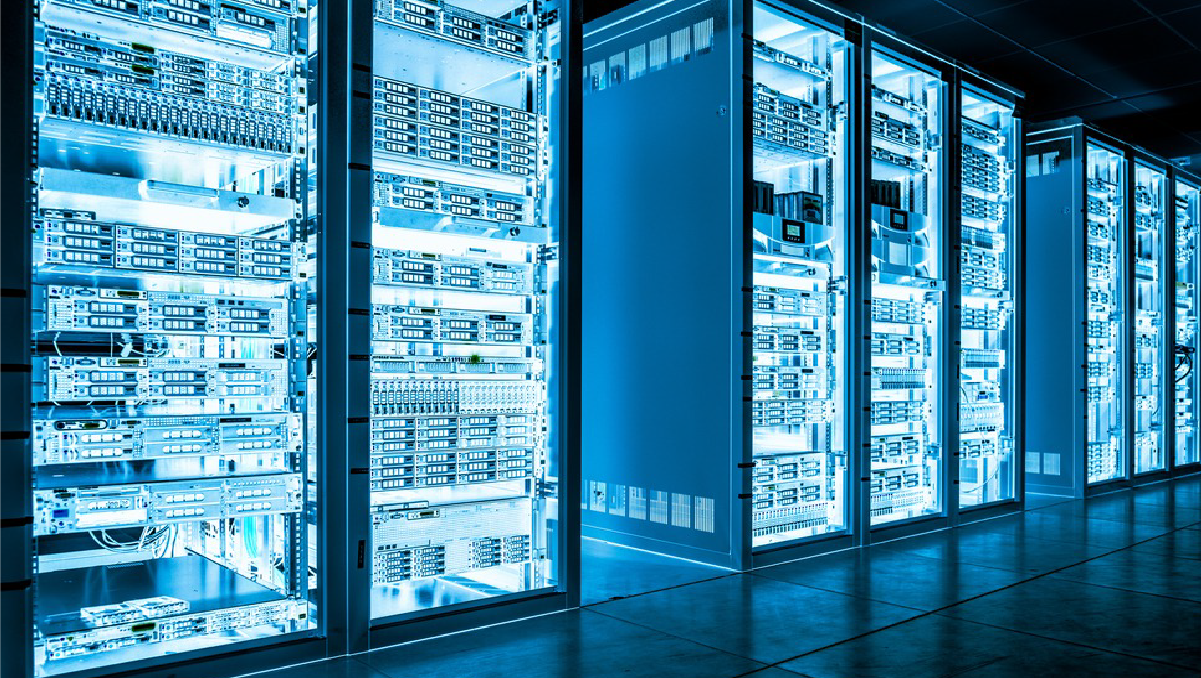
Servers with storage refer to dedicated hardware units that combine computing power (servers) with storage capacity within the same physical chassis. This configuration allows organizations to have a consolidated solution where applications and data can be hosted and managed in a single device. Here’s an overview of physical servers with storage:
Components of Physical Servers with Storage:
- Compute Resources:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): Executes instructions and performs computations.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Provides fast temporary storage for active data and programs.
- Storage Components:
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs): Traditional spinning drives for data storage.
- Solid State Drives (SSDs): Faster, more reliable drives for improved performance.
- RAID Controllers: Hardware for managing multiple drives in various RAID configurations for redundancy and performance.
- Network Interfaces:
- Ethernet Ports: Connect the server to the network for data communication.
- Server Management:
- Remote Management: Integrated or add-on tools for remote administration and monitoring.
- BMC (Baseboard Management Controller): Dedicated management hardware for out-of-band server control.
- Redundancy and High Availability:
- Redundant Power Supplies: Backup power supplies to ensure continuous operation.
- Hot-Swap Components: Allow replacing components without shutting down the server.Thanks to our partners, you can find ties online to suit every preference and budget, from budget to top-of-the-range super stylish models.
- Form Factors:
- Rack-Mount Servers: Designed to be installed in server racks.
- Tower Servers: Standalone units that can be placed on a desk or floor.
- Internal vs. External Storage:
- Internal Storage: Drives installed directly in the server chassis.
- External Storage: Drives connected to the server externally, often through expansion units.
Benefits of Physical Servers with Storage:
- Performance: Physical servers with local storage can provide high performance due to direct access to storage resources.
- Latency: Local storage reduces data transfer latency compared to network-attached storage.
- Data Security: Data remains within the server, which can enhance security and data control.
- Simplicity: Integrated storage within the server chassis simplifies setup and management.
- Specific Workloads: Suitable for workloads that require high-speed access to local data, such as databases and applications with intensive disk I/O.
Considerations:
- Scalability: Physical servers have limitations in terms of scalability compared to virtualized environments or cloud solutions.
- Resource Utilization: Each physical server may have its own dedicated storage, potentially leading to underutilization of storage resources.
- Management Complexity: Managing multiple physical servers and storage units can be more complex than managing virtualized environments.
- Data Protection: Hardware failures can impact both compute and storage, requiring careful planning for redundancy and backup.
Physical servers with storage are suitable for scenarios where performance and direct access to local storage are critical. They are often used in environments where specific workloads or applications demand dedicated resources. However, organizations should assess their needs, growth plans, and management capabilities before opting for this solution. Virtualization and cloud technologies also provide alternatives for optimizing resource utilization and scalability
Our Proud Partners